Trends in Compensation and Operational Practices for Plastic Processors
by Troy Nix
MAPP, Inc.
2014 Wage and Benefits Survey
Accumulated payroll and benefit data in MAPP's study was submitted by company owners, presidents, human resource directors and senior staff level professionals. For more information, visit the Publications tab at www.mappinc.com.
The Manufacturers Association for Plastics Processors (MAPP) has just released its latest report on compensation and benefit trends in plastics processing. Known as the most comprehensive study in the industry, MAPP's 2014 report is one that has evolved over the last 11 years and remains the only report completely devoted to the plastics manufacturing sector. Today, the publication contains comprehensive analysis on over 50 different job classifications and represents data in excess of 14,500 hourly and salaried employees located in 32 states across America.
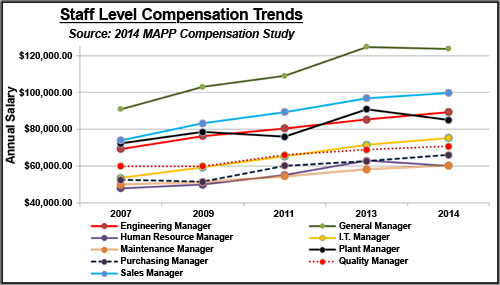
Compensation trends for staff level team
The total median annual compensation for a grouping of nine staff level positions, including the following, provides a basis for trend data over the last seven years.
1. Engineering manager
2. General manager
3. Human resource manager
4. IT manager
5. Maintenance manager
6. Plant manager
7. Purchasing manager
8. Quality manager
9. Sales manager
Considered the most common staff level positions held in any size of company, the total combined payroll for these nine job functions has increased by 25.7 percent since 2007. Today, the combined median payroll of these nine job classifications is $730,881. That amount increases by approximately 3.7 percent on an annual basis. Graph 1 represents the compensation trend for each of these individual job functions.
Of the 53 job classifications tracked in the 2014 Wage and Compensation Study, over 70 percent contained wage/salary rate changes under five percent over the last 12 months. Job descriptions that experienced the largest adjustment in wages and salary over the last twelve months included CFOs, delivery drivers, machinists, marketing directors and TS/ISO coordinators.
Job titles experiencing negative growth or growth below inflationary rates in the last year include, but are not limited to, administrative assistant, general manager, plant manager, machine operator, mold setter and more. Negative growth in compensation partly is due to changes in the survey population and combined with actual employment changes at the company level.
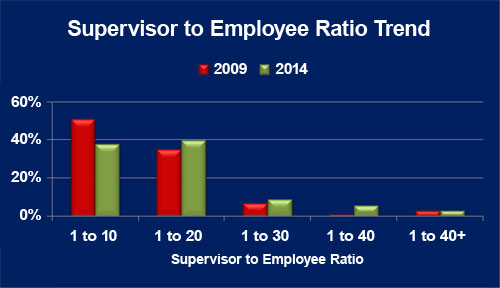
Supervisor to employee ratio
As companies look to gain any competitive edge possible, the innovation in capitalizing on machine utilization and employee capacity can be seen by examining slight changes in both shift structures and the supervision per employee ratio trends over the last five years.
One evident trend focuses on the increased efficiency of the uses of supervision. Over the last five years, plastics processors have steadily increased the role of individual supervisors by expanding the number of employees each is responsible for managing. In 2009, nearly 52 percent of company executives reported a supervisor to employee ratio of 1:10. Today, only 38 percent of executives report using a supervisor to employee ratio of 1:10, representing a 14 percent decrease in the last five years. Now, the most common supervisor to employee ratio is 1:20, while nearly one in five plastics manufacturing company executives use a 1:30 or above supervisor to employee ratio, which nearly doubles that reported five years ago (Graph 2).
Operational shift structure
Although one quarter of plastics manufacturing companies across the nation continue to use one- and two-shift operations, 62 percent of business leaders commonly use a three-shift operation over a five-day work week. Sixteen percent of the population using this three-shift, five-day-per-week operating strategy also uses a tactic to enhance their shift structure by providing weekend coverage in order to continue production on specific jobs. To successfully staff second shift operations, nearly one in three companies provide their employees with increased compensation ranging between $.26 to $.50 per hour, with 25 percent providing $.25 or less. The second shift premium rate has grown by over 20 percent over the last five years; however, third shift premium rates essentially have stayed the same, with 18 percent of respondents providing $.25 or less and 29 percent providing between $.26 to $.50 per hour.